Angry Films, Kintop Pictures, Preger Entertainment
Michelle Smith, Monash University
An 18-year-old girl prepares to die to enable the birth of her half-vampire baby. Her spine is broken in the process, and the fanged baby begins to gnaw its way through her stomach before the girl’s husband performs a vampiric Cesarean section. This is a crucial moment in Stephenie Meyer’s Twilight novel series, published from 2005 to 2008.
Meyer’s books heralded a new, and continuing, wave of Gothic fiction for Young Adult readers, which revisits familiar literary Gothic conventions: ancient, ruined buildings and monstrous supernatural figures like the vampire, werewolf, ghost and witch.
The Gothic romances of the 18th century, such as the novels of Ann Radcliffe, and the enduringly popular Bram Stoker’s Dracula (1897), sought to recreate feelings of terror and horror for an audience of adult readers. Today, however, most Gothic fiction is being published for, and read by, young people. Surprisingly, it has proved to be the ideal genre for exploring the grotesque and frightening aspects of coming of age, and metaphorically representing pressing social issues such as racism and gender inequality.
Read more:
Friday essay: what might heaven be like?
The phenomenally popular YA genre, targeted at readers between 12 and 18 years old, evolved from realist novels of the 1960s. These books were preoccupied with the struggles of adolescence set against a backdrop of social issues. Now, though, the genre often looks to the supernatural. Beyond Twilight, some of the most popular YA Gothic series also focus on the “lives” of vampires who are protagonists rather than foes.
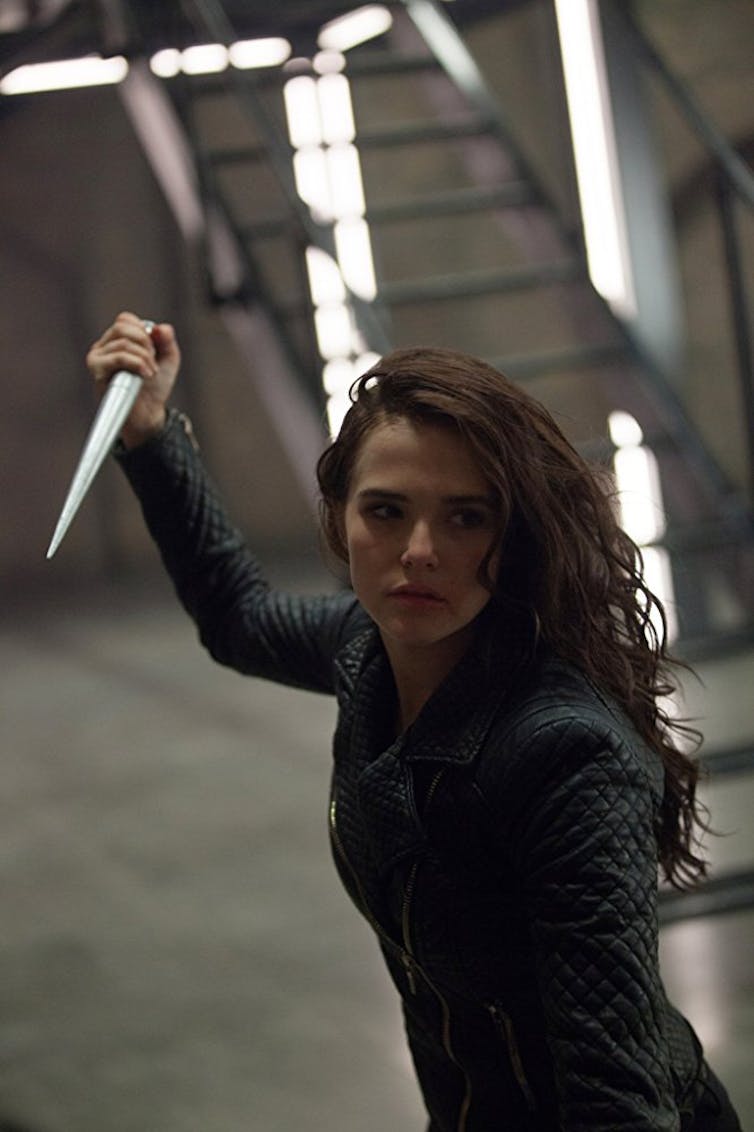
Richelle Mead’s six-book Vampire Academy (2007-2010), now adapted into a TV series, is about a teenage girl who is a Dhampir (half-human, half-vampire). She becomes entangled in a forbidden romance with her instructor as St Vladimir’s Academy, while learning how to defeat evil vampires named Strigoi.

idmb
The YA Gothic revival has also embraced a wide range of supernatural entities. Cassandra Clare’s Shadowhunter Chronicles, a cross-media franchise that includes the Infernal Devices and Mortal Instruments novel series, charges angel-blooded humans with the task of protecting regular humans from a range of supernatural beings.
The Nephilim, or Shadowhunters, are busy controlling demons, warlocks, werewolves, faeries and vampires, but critically, it is their part-supernatural status that enables them to serve as protectors.

Clare has said that she did not write her series for young adults (and indeed almost half of the readership of YA fiction might be adults). Nevertheless, her teenage protagonists have resonated with readers of the same age.
The Gothic, and its newer sub-genres like paranormal romance, have a unique resonance with teenagers. They are poised in a transitional space between childhood and adulthood, neither quite embodying the stage they are leaving behind nor fully the thing that they are in the process of becoming. It is unsurprising, then, that they have eagerly embraced the Gothic’s themes of the liminal and the monstrous, as well as its fixation on romance and sex.
Another significant element of the current YA Gothic revival is the emergence of the girl monster. In earlier manifestions of the “female Gothic”, first published in the 18th century by women writers, female protagonists were often courageous, but simultaneously passive and victimised. The plots of the female Gothic reflected the comparative powerlessness of women at the time and their fears about their vulnerability and entrapment within domestic roles and patriarchal society.
In contemporary YA Gothic, girl monsters, who can constitute a threat to others and themselves, disrupt the plotline of male monster and female victim.
Why now?
The most obvious catalyst for the embrace of Gothic conventions in literature for young people is J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series. Its popularity signalled a warm embrace of fantasy fiction that confronted the eternal dilemma of the battle between good and evil, charging a child – and later teenage protagonist – with the ability to save the world. While Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry was not necessarily Gothic, the Potter phenomenon opened the way for the publication of numerous titles that embraced the possibilities of young protagonists with supernatural abilities.
Read more:
Rethinking Harry Potter twenty years on
Most significantly, Meyer’s Twilight series about human Bella Swan and “sparkling” vampire Edward Cullen, combined this staple figure of Gothic fiction with the teen romance novel. The Twilight novels were bestsellers internationally and the saga was voted into the number one position in Australian book chain Angus & Robertson’s Top 100 Books poll of 2010. The Twilight universe expanded from books into a highly successful film series.

Summit Entertainment, Temple Hill Entertainment, Maverick Films.
The Gothic has had several major periods of popularity since its first appearance in 18th-century England, with Horace Walpole’s novel The Castle of Otranto (1764). In each subsequent revival of Gothic fiction, the genre has been reworked and reinvented to address current cultural concerns.
In particular, the monsters that haunt the pages of Gothic novels are transformed with shifting fears and anxieties. In her influential book Our Vampires, Ourselves Nina Auerbach explains that “every age embraces the vampire it needs”, and this comment can be extend to Gothic monsters more generally.
Contemporary YA fiction blurs the line between good and evil. In Gothic novels of the 19th century, monsters were usually wholly “Othered”. A Victorian-era vampire such as Stoker’s Dracula, for instance was depicted as evil, foreign, and frighteningly different to the British human.

American Zoetrope, Columbia Pictures Corporation, Osiris Films
But contemporary monsters are no longer necessarily imagined as racially different or set in opposition to the human. Moreover, they are often represented sympathetically, especially in stories told from their perspective.
These include the iZombie comic series, in which the protagonist must eat brains on a monthly basis to survive, and Claudia Gray’s Evernight series, in which the reader is not even aware that the girl protagonist is a vampire for half of the first book. Indeed, as Anna Jackson explains in New Directions in Children’s Gothic, “the monsters have become the heroes” in contemporary children’s Gothic.
The passive heroine
Most Gothic novels for young people contain a romance plot. This is often because the protagonists’ age places them in the transitional zone for entering adulthood, which is demarcated by sexual experience.
Read more:
How long have we believed in vampires?
In a typical YA Gothic novel, such as Twilight, a plot in which a human or monstrous girl protagonist falls for a boy who is not her “type” can dissolve the boundaries between monster and human. These monstrous love interests range from traditional Gothic ones – vampires, werewolves, zombies, ghosts and witches – to newer figures such as fallen angels and faeries. The key challenge to be overcome in these novels is the barriers posed to love by supernatural monstrosity, including the physical dangers to humans, as well as social discrimination about “cross-species” love.
In one of few major studies of teen romance fiction, published almost 30 years ago, Linda Christian-Smith described these novels as a “site of ideological struggles for young women’s hearts and minds”. In particular, she refers to teen romance fiction’s emphasis on heteronormative coupling and motherhood. Little has changed with respect to depictions of sexuality since, despite the YA Gothic’s embrace of diverse human-monster relationships.
Most romances in the genre are heterosexual. They do often emphasise the heroine’s agency through her supernatural abilities and ability to choose between men or move between relationships. However, the human heroines of the Twilight series and Lauren Kate’s Fallen series, in which the heroine becomes drawn to a boy who is a fallen angel, are comparatively indecisive and continue to need rescuing.
Tellingly, Joss Whedon, the creator of the TV series Buffy, The Vampire Slayer (1997-2003), has described Twilight’s Bella as lacking empowerment, overly fixated on her romantic options, and “completely passive”.

Summit Entertainment, Temple Hill Entertainment, Maverick Films.
Novels with passive human heroines allow the reader to use the fantasy of romance as a temporary escape from real-world gender inequality. Yet they also reinforce its reality for female readers.
The girl monster
Supernatural heroines, however, are often able to breach the confines of traditional femininity and become extraordinary in ways that Twilight’s Bella and other human characters cannot. In a number of YA Gothic novels, such as Mead’s Vampire Academy, the protagonists disrupt expectations of feminine behaviour because of their unique, and often poorly understood, supernatural abilities. These special powers become the focus of anxieties about the girls’ coming of age, as they pursue romances that place their broader communities under threat.
The Vampire Academy series was sufficiently popular in 2010 for three of its six titles to sell between 300,000 and half a million copies in hardcover in the US alone, according to Publishers Weekly. However, unlike the Twilight series, on which it likely attempted to capitalise, its protagonist, Rose, is half-vampire, half-human and a monster in her own right. Rose shares a close bond with vampire Lissa, and is driven to break the Academy’s rules in order to save her friend when she is kidnapped, highlighting that girls are also capable of protecting and rescuing people they love.

idmb
Vampire Academy positions Rose as a sexual object, particularly in the eyes of a privileged type of vampire (Moroi), who find Dhampir women especially attractive because of racial differences. Rose enjoys her sexuality and dresses to take advantage of it, but this sexuality operates within her definition as a strong young woman:
First they saw my body and the dress. Testosterone took over as pure male lust shone out of their faces. Then they seemed to realize it was me and promptly turned terrified. Cool.
Rose is able to reject unwelcome advances and possesses the physical strength and skills to stand up for herself, suggesting a fantasy of empowerment and equality.
Lissa, meanwhile, thwarts what amounts to an attempted gang rape of a drugged girl. A group of male Moroi students attempt to take advantage of a female feeder (person who permits their blood to be sucked) at a party, “doing a sort of group feeding, taking turns biting her and making gross suggestions. High and oblivious, she let them”.
The supernatural female protagonists in YA gothic novels are responsible for their own safety and protection, yet they also have a responsibility to keep others safe.
These heroines have some romantic and sexual agency in a way that can be considered progressive. However, their desire is also framed as disruptive and dangerous and there is an obsessive fixation on the pursuit of romance above the girl’s own development, education and safety.
In other words, the superficially radical potential of girl heroines with superhuman physical strength, mind-reading abilities, and the potential to kill can merely be a decorative smokescreen for the reinforcement of traditional feminine values.
The good and monstrous within
The recent proliferation of Gothic YA novels is skewed toward a female readership with a focus on girl protagonists, and significant emphasis on their quest for romance. Nevertheless, there are a number of series with boy heroes. For example, Ransom Riggs’ Miss Peregrine’s Home for Peculiar Children (the first book of which was recently filmed by director Tim Burton), focuses on a 16-year-old human boy, Jacob.

Twentieth Century Fox, Chernin Entertainment, TSG Entertainment.
Jacob has inherited an ability that makes him uniquely able to help the supernatural peculiar children of the title, who are threatened by creatures named hollowgasts who are driven to murder peculiar children in order to feed upon their souls. For Jacob, his transition to adulthood is less about romance and more about self-discovery, connections with his ancestors, and finding a way to negotiate his new-found abilities and responsibilities.
In The Gothic Child, Maria Georgieva suggests that the traditional Gothic novel is preoccupied with “the growth and transformation of the child, the crisis of adolescence and the sometimes painful transition into adulthood”. She is referring to the child’s potential to grow into the hero, heroine or villain.
However, the recent surge in YA Gothic fiction takes this fascination with the darker aspects of childhood in a different direction. The girl heroine, in learning to manage the physical and emotional shifts of her development and more complex relationships in romance, can both be a threat and a saviour to others.
The fuzziness of her nature reflects both the liminal status of the teenager and new cultural understandings of the monster, who now more often resembles the typical American teen than an undead Romanian count.
![]() Instead of contemplating a child’s potential to head towards either good or evil, recent Gothic YA acknowledges the possibility of both the good and the monstrous residing in one person.
Instead of contemplating a child’s potential to head towards either good or evil, recent Gothic YA acknowledges the possibility of both the good and the monstrous residing in one person.
Michelle Smith, Senior Lecturer in Literary Studies, Monash University
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.